In any firm, controlling revenue is essential for sustainable growth and economic stability. The revenue pattern encompasses the entire method from the initial client relationship to the final collection of payment. It requires different stages and activities that finally determine the financial health of the organization. In this short article, we shall investigate the revenue period in more detail, discussing their essential parts, issues, and techniques for optimizing financial performance.
Introduction to the Revenue Period:
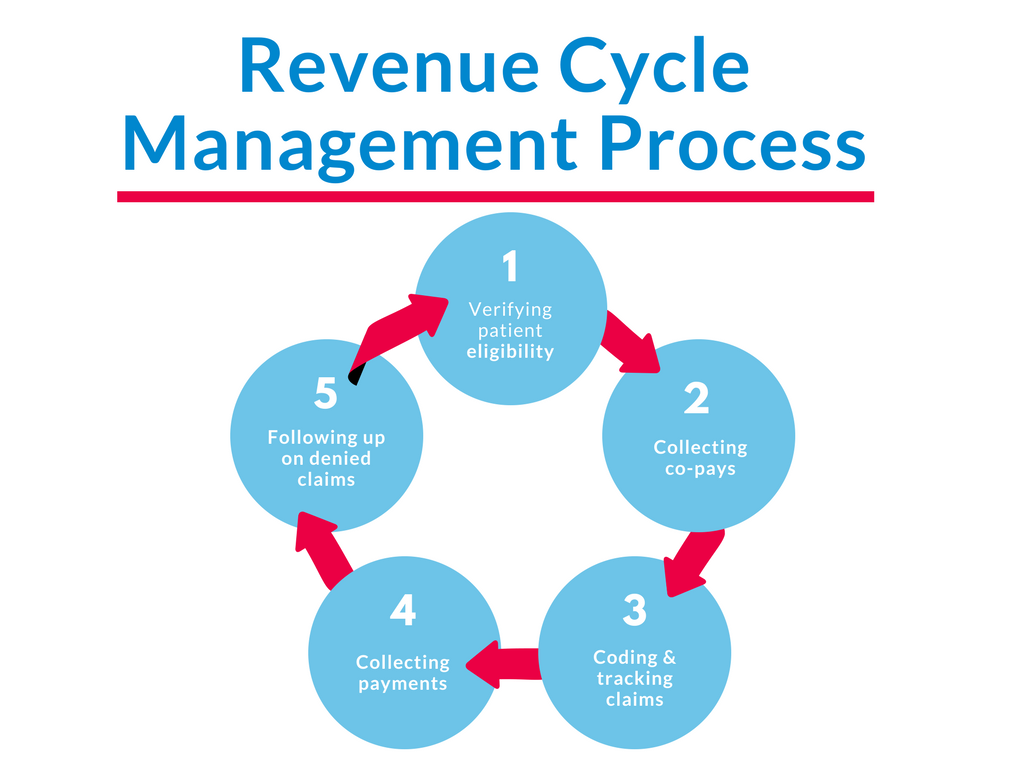
The revenue routine shows the trip of revenue era inside an organization. It on average starts with lead technology and marketing initiatives and advances through income, order handling, invoicing, cost selection, and reconciliation. Each stage in the revenue cycle plays a critical role in ensuring precise and appropriate revenue recognition.
Key Aspects of the Revenue Cycle:
a. Lead Era and Marketing: Getting potential clients and making attention about services and products or services.
b. Income and Customer Exchange: Changing leads in to customers through efficient revenue strategies and negotiations.
c. Order Running and Fulfillment: Obtaining and handling client instructions, ensuring precise solution distribution or service fulfillment.
d. Invoicing and Billing: Generating invoices for items or companies made, including ideal pricing and terms.
e. Records Receivable Management: Checking and gathering RCM service provider payments from clients, managing credit phrases and payment terms.
f. Revenue Recognition and Confirming: Realizing revenue centered on sales rules and rules, ensuring exact financial reporting.
Challenges in the Revenue Pattern:
Managing the revenue cycle successfully is not without their challenges. Some typically common challenges include:
a. Wrong Data and Paperwork: Incomplete or incorrect may cause delays in invoicing and cost collection.
b. Billing and Coding Mistakes: Problems in billing or development can lead to cost rejections or setbacks, impacting money flow.
c. Regular and Efficient Communication: Lack of obvious interaction between divisions could cause delays or misunderstandings in the revenue cycle.
d. Complicated Cost Systems: Coping with diverse cost strategies, running fees, and reconciling transactions may be time-consuming and error-prone.
e. Submission and Regulatory Needs: Sticking with industry-specific regulations and accounting requirements may be complicated and involve continuing monitoring.
Techniques for Optimizing the Revenue Routine:
To increase economic success and assure a smooth revenue pattern, agencies can implement the following strategies:
a. Streamline Operations: Recognize bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the revenue routine, and improve functions to cut back setbacks and improve productivity.
b. Accept Engineering: Implement effective revenue cycle administration application and automation resources to enhance precision, pace, and efficiency.
c. Enhance Data Accuracy: Spend money on information validation and quality get a grip on procedures to reduce errors and differences in customer information and billing details.
d. Increase Communication and Relationship: Foster successful transmission and cooperation between sectors active in the revenue routine to reduce misconceptions and delays.
e. Check Important Performance Indicators (KPIs): Build and monitor relevant KPIs such as for instance days revenue fantastic (DSO), collection costs, and revenue development to evaluate and improve economic performance.
f. Staff Teaching and Education: Offer continuous teaching and training to personnel active in the revenue period to make certain a deep understanding of techniques, compliance, and most useful practices.
Realization:
The revenue cycle is a crucial aspect of economic management and organizational success. By knowledge the important thing components, difficulties, and applying powerful methods, companies can enhance their revenue cycle, improve money movement, improve customer care, and achieve long-term economic stability. Continuous tracking, adaptation to market improvements, and a commitment to method improvement are important for companies to thrive in today’s competitive company landscape.
